Introduction To Compiler Design, What is Compiler, Preprocessor, Assembler, Interpreter, Advantages of Compiler, Loader and Link-Editor
Introduction To The Compiler Design
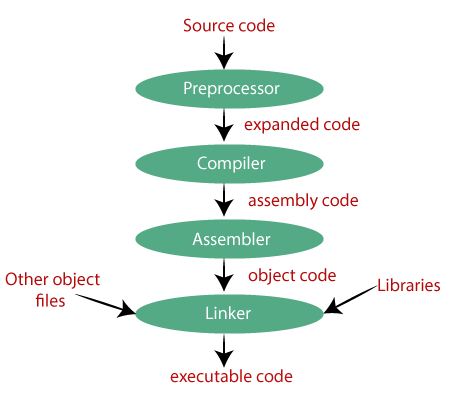
What is Compiler?
-A compiler is a special program that translates the source code of a programming language into
machine code, bytecode, or another programming language. The source code is usually written in
a high-level human-readable language, such as Java or C++.
The computer is an intelligent combination of software and hardware. Hardware is simply a piece
of mechanical equipment and its functions are being compiled by the relevant software. The
hardware considers instructions as electronic charge, which is equivalent to the binary language in
software programming. The binary language has only 0s and 1s. To enlighten, the hardware code
has to be written in binary format, which is just a series of 0s and 1s. Writing such code would be an
inconvenient and complicated task for computer programmers, so we write programs in a high-level language, which is convenient for us to comprehend and memorize. These programs are then
fed into a series of devices and operating system (OS) components to obtain the desired code that
can be used by the machine. This is known as a language processing system.
Preprocessor
-The preprocessor includes all header files and also evaluates whether a macro(A macro is a piece
of code that is given a name. Whenever the name is used, it is replaced by the contents of the
macro by an interpreter or compiler. The purpose of macros is either to automate the frequency
used for sequences or to enable more powerful abstraction) is included. It takes source code as
input and produces modified source code as output. The preprocessor is also known as a macro
evaluator, processing is optional that is if any language that does not support #include and macros
processing is not required.
Compiler
- Compiler is a translator program that translates a program written in (HLL) the
source program and translates it to an equivalent program in (MLL) the target program. An
important part of a compiler is the error that is displayed to the programmer.
The execution of a program written in the HLL programming language basically consists of two
parts. the source program must first be compiled into an object program. The result object
program is then loaded into an executed memory.
Assembler
- Programmers found it difficult to write or read programs in machine language.
They begin to use a mnemonic (symbols) for each machine instruction, which they would later use
translate into machine language.
Such a mnemonic machine language is now called assembly language.
Programs known as assemblers were written to automate the translation of assembly language into machine language.
The input to an assembly program is called a source program, and the output is a machine language
translation (object program).
Interpreter
-An interpreter is a program that appears to execute a source program as if it
were machine language
Languages such as BASIC, SNOBOL, and LISP can be translated using interpreters. JAVA also uses
an interpreter. The process of interpretation can be carried out in the following phases.
- Lexical analysis
- Syntax analysis
- Semantic analysis
- Direct Execution
Advantages
- Modification of the user program can be easily performed and implemented as execution proceeds.
The object type denoting multiple can change dynamically.
Debugging a program and finding errors is a simplified task for a program used for interpretation.
The language interpreter makes it machine independent.
Disadvantages
-The Program execution is slower.
Memory consumption is more.
Loader and Link-Editor
- Once the assembler processes an object program, that program must be placed in memory and
executed. The assembler could put the object program directly into memory and transfer control to it.
Thus causing the program to be executed in machine language. This would waste the kernel by leaving
the assembler in memory while the user program was running. Also, the programmer would have to re-translate his program with each execution, thus wasting translation time. To overcome these problems
of wasted translation time and memory. System programmers developed another component called a
loader "A loader is a program that places programs in memory and prepares them for execution."
It would be more efficient if the subroutines could be translated into object form, and the loader
could be "relocated" directly behind the user program. The task of adjusting programs so that
they are not placed in arbitrary central locations is called relocation. Relocation chargers
perform four functions.
Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.