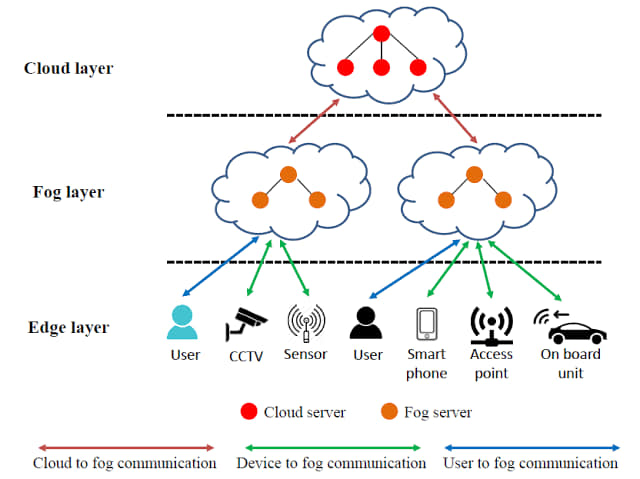
Fog Computing:
Fog computing is a decentralized computing infrastructure that extends cloud computing capabilities to the edge of the network. It involves distributing computing, storage, and networking resources closer to the data source, reducing latency, and improving efficiency for applications and services. Fog computing is often seen as an intermediate layer between the cloud and end devices.
Key Concepts and Components:
1. Edge Devices:
- Fog computing extends computing capabilities to devices at the edge of the network, such as sensors, IoT devices, and gateways.
2. Fog Nodes:
- These are computing nodes deployed at the network's edge, providing resources for processing, storage, and networking.
3. Proximity to Data Source:
- Unlike cloud computing, which centralizes resources in remote data centers, fog computing brings computing resources closer to the data source, reducing latency.
4. Real-Time Processing:
- Fog computing is well-suited for applications that require real-time or low-latency processing, such as IoT, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality.
5. Distributed Architecture:
- Fog computing involves a distributed architecture with multiple fog nodes working collaboratively, complementing cloud resources.
6. Scalability:
- Fog computing allows for scalability by distributing computing tasks across multiple edge devices, preventing overburdening a centralized cloud infrastructure.
7. Use Cases:
- IoT Applications: Fog computing is beneficial for processing data generated by IoT devices at the edge, reducing the need to send all data to the cloud.
- Smart Cities: Applications like smart traffic management, surveillance, and energy monitoring can benefit from fog computing.
- Healthcare: Enables real-time processing of health data from wearable devices and medical sensors.
8. Challenges:
- Security: Ensuring the security of distributed resources and data at the edge.
- Interoperability: Integrating diverse devices and platforms within a fog computing environment.
- Resource Management: Optimizing the allocation of computing resources across fog nodes.
9. Complementary to Cloud Computing:
- Fog computing works with cloud computing, where certain tasks are offloaded to the cloud while others are processed locally at the edge.
Benefits of Fog Computing:
1. Low Latency:
- Processing data closer to the source reduces latency and supports real-time applications.
2. Bandwidth Efficiency:
- Fog computing minimizes the need to send large volumes of data to the cloud, optimizing bandwidth usage.
3. Improved Reliability:
- Distributed architecture enhances reliability by reducing the impact of a single point of failure.
4. Scalability and Flexibility:
- Fog computing allows for flexible and scalable resource deployment based on edge applications' specific needs.
Fog computing addresses the limitations of relying solely on centralized cloud resources, providing a more efficient and responsive computing paradigm for edge and IoT applications.

Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.